18.01.2021
A Trap for Nematodes
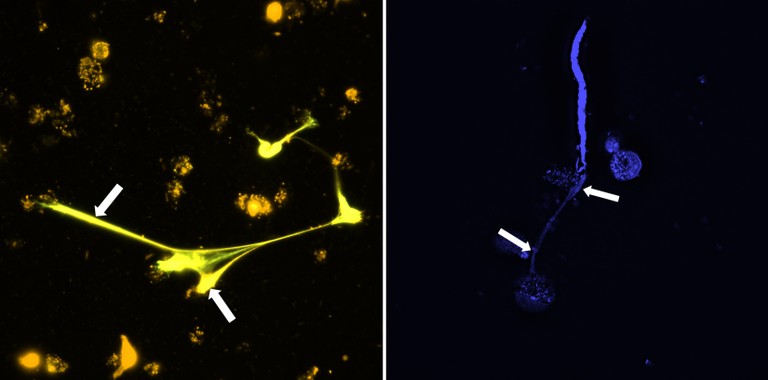
Filariae, slender but sometimes up to 70 centimeters long nematodes, can set up residence in their host quite tenaciously and cause serious infectious diseases in the tropics. The tiny larvae of the worms are usually transmitted from person to person by mosquitoes, which pick up the larvae from the blood or subcutaneous tissue when they bite and deposit them in the vessels or tissues of their next victim. Researchers led by the University of Bonn have now investigated a mechanism by which the immune system attacks the filariae. Certain immune cells, the eosinophil granulocytes, release DNA that forms a kind of web around the larvae and traps them. The researchers also identified which protein "turns on" the mechanism, known as the Dectin-1 receptor. The study has been published in the journal Cell Reports DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108621 .
© Alexandra Ehrens


